Copyright 2023 Vernon R Stanley, MD, PhD | Taken from the Comprehensive 12-lead ECG Interpretation Course (30 hrs Cat I CME/CE) & the STEMI ECG Recognition Review Course (6 hrs Cat I CME/CE).
In this blog post, we will compare four tracings and discuss the phenomenon of Terminal QRS Distortion as outlined below.
First, try the following Pre-Quiz (Click Here).
Following the analysis of these 4 12-lead ECG tracings, we will present a guideline to aid you as you search for the STEMI, especially when the differential diagnosis has been narrowed down to the acute STEMI vs a benign early repolarization pattern.
This is a sobering task since one patient will be referred to the cardiac catheterization lab and while the other might be discharged home or simply admitted for observation. The patient’s disposition hinges on your interpretation of the 12-lead ECG.
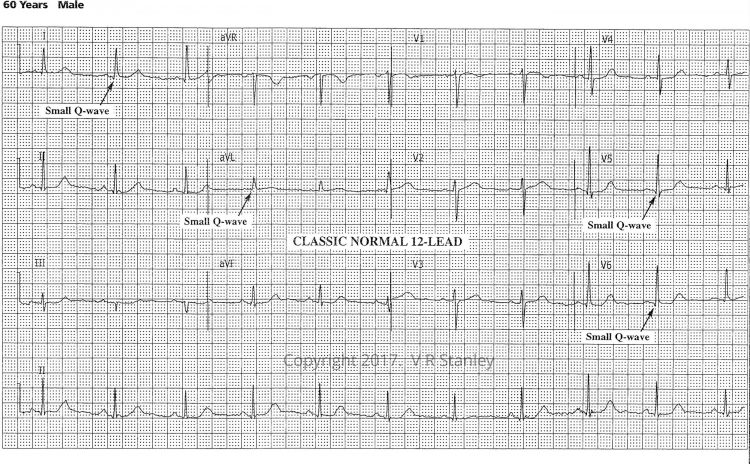
Please refer to the ECG below as an example of a Classic Normal 12-lead ECG. Let us focus on the terminal portion of the QRS complexes. Specifically, I want you to note the following:
- The right-most precordial ECG leads V1, V2, V3 take on an rS configuration (r << S in Lead V1)
- The left-most precordial ECG leads V4, V5, V6 take on a qR configuration (depth of q << R in Lead V6)
The dominance of these voltages fluctuates as you go back and forth across the precordium i.e. crescendo and decrescendo of the R-wave and S-wave. We acknowledge this phenomenon when we refer to R-wave progression noting that the hypothetical position on the precordium where R = S is the transition zone. It is clearly true that the transition zone of this ECG tracing lies between Lead V3 and Lead V4. We will agree that the normal transition zone occurs between Lead V2 and Lead V4 inclusive. The transition zone of this tracing is therefore normal.
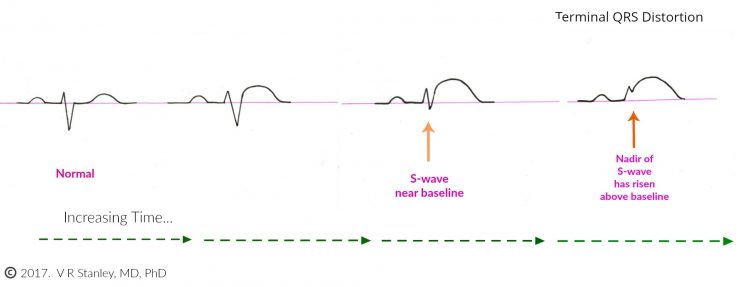
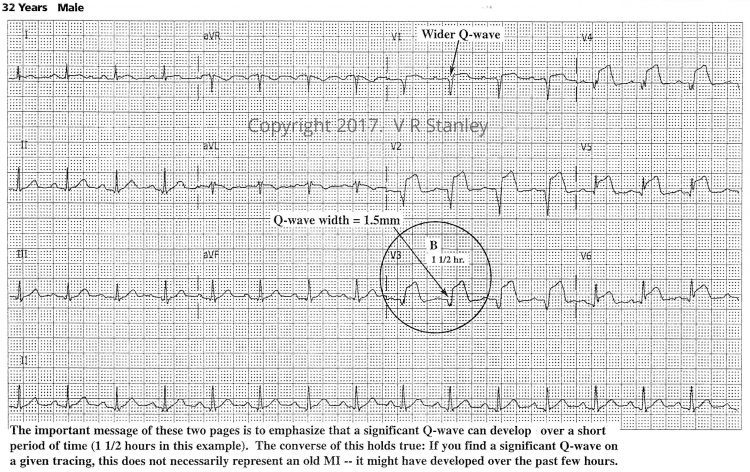
Sometimes during the evolution of the acute Anterior STEMI (ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction) on the 12-lead ECG, you will see the terminal S-wave begin to rise toward the baseline. When the terminal S-wave rises above the baseline then it technically is no longer an S-wave. When this occurs, it is described as “terminal QRS distortion”. The phenomenon of terminal QRS distortion is highly suspicious of the Acute STEMI (this statement holds especially true of Leads V2, V3).
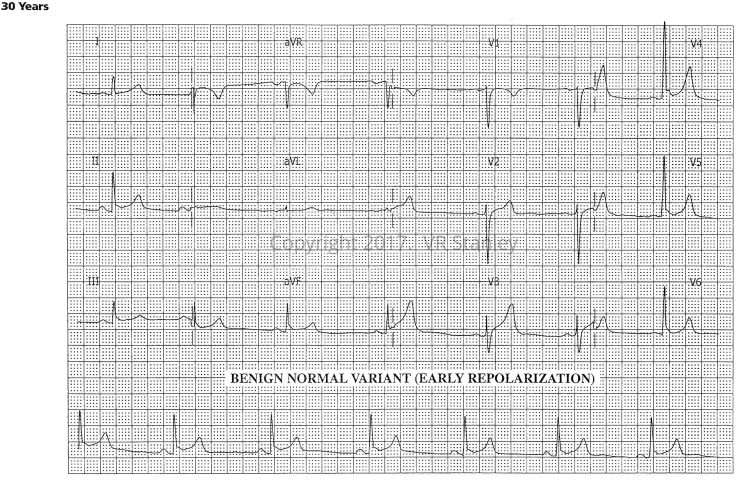
NOTE: An exception to this rule occurs when the take off of the J-point forms the shape of a “fish hook” (J-wave). If this J-wave is present, the probability shifts in the direction of a benign normal variant on the 12-lead ECG (BER or early repolarization).
The rising of the nadir of the S-wave is demonstrated in the Illustration below:
Similarly, if the QRS complex takes on a qR configuration, you might observe the following phenomenon. As the acute STEMI evolves, the J-point take off will rise with time. When the J-point rises to > 50% the R-wave height it is called “terminal QRS distortion”.
This is highly suspicious of the acute STEMI (this holds especially true of Leads V5, V6; the exception again occurs if a J-wave is present). This rising of the J-point is shown schematically in the Illustration below.
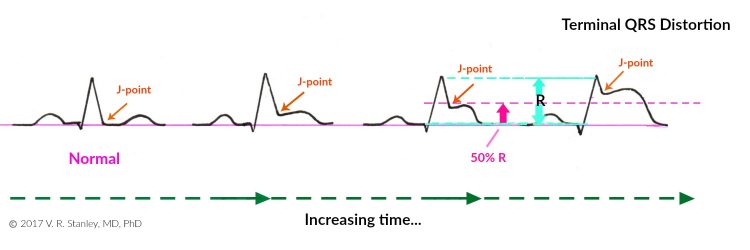
NOTE: The two Illustrations above focus on the ST-segments. Particularly note that I have depicted the ST segments as concave down. Be aware that most commonly the ST-elevations of the acute STEMI are indeed concave down; however, they certainly might be concave up. When this occurs, you can see why this might be problematic to decide whether a given 12-lead ECG tracing is that of an acute STEMI or and ECG of benign early repolarization (BER) pattern.
We will now compare four 12-lead ECG tracings using the following chart (see below for ECG Tracings):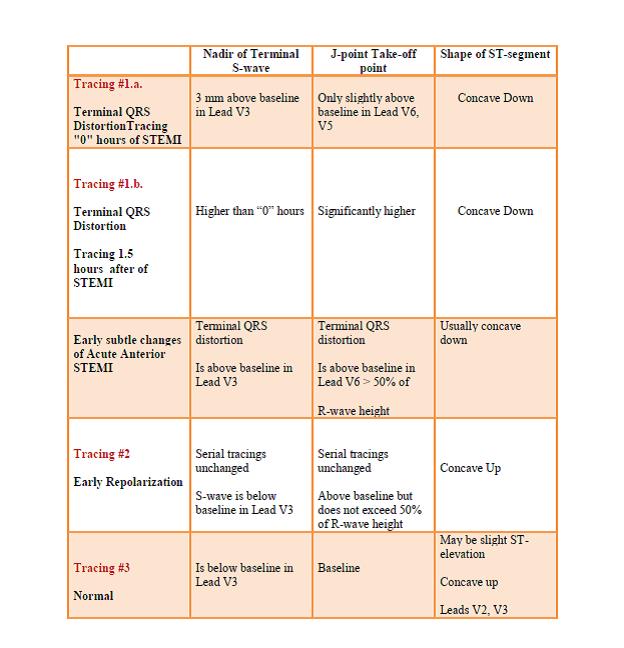
12-lead ECG Tracing #1.a Hour “0”
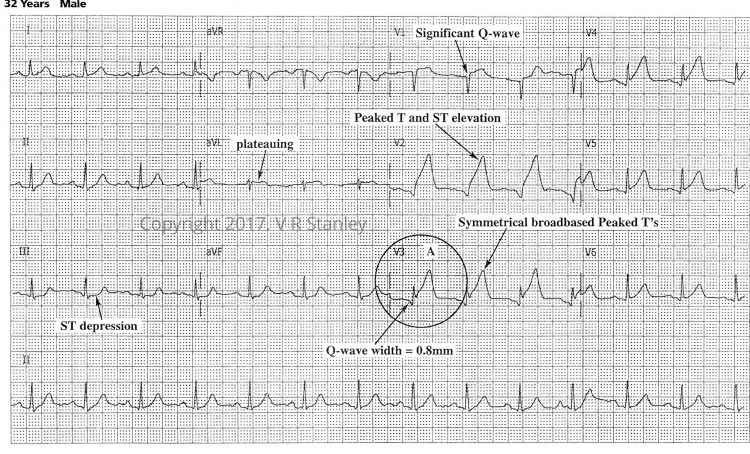
Tracing #1.b. – at “1.5” hours evolving STEMI (same patient)
Tracing #2 – Early Repolarization (Benign Normal Variant)
Tracing #3 – Normal ECG

Conclusion: When faced with the challenge of deciding whether a given 12-lead ECG tracing is early repolarization (BER) or acute STEMI (especially if the changes are subtle), look for “terminal QRS distortion”. If present, it is highly suspicious for the Acute STEMI.
CLINICAL PEARL: The discussion below is especially useful when the changes on the cardiogram are subtle.
In your search for the acute STEMI you will frequently be faced with the uncomfortable differential diagnosis of:
- Acute Anterior MI OR
- Benign Normal Variant (early repolarization)
This look-alike scenario occurs because we know that frequently the ST-segment elevations of the acute MI are concave up (catenary shaped), although more often than not they are concave down (tombstone –like), as is the case with the early repolarization pattern. This concave “upness” of the ST-segment across the precordium can make these two ECG patterns very much look alike so that only the discriminating eye can unravel.
At this juncture, I advise you to consult with two Leads of the full 12-lead ECG: Lead V2 and Lead V3
- If terminal QRS distortion is present in Lead V2 or Lead V3 AND
- If a J-wave is absent in both Leads →→→→ It is highly probable that the interpretation is “Acute STEMI” (LAD artery occlusion).
*Terminal QRS distortion is defined as absence of the S-wave (S-wave has risen above the baseline).
As always you must adhere to a strict regimen for each patient of:
- Clinical correlation
- Comparison with old 12-lead ECG tracings and old medical records
- Serial 12-lead ECG tracings, cardiac markers as needed
*Referenced from the following:
- http://hqmeded-ecg.blogspot.com/2015/10/best-explanation-of-terminal-qrs.html steve smith MD 2015
- http://hqmeded-ecg.blogspot.com/2015/10/best-explanation-of-terminal-qrs.html 2015
- Brooks-Walsh
- Steve Smith, MD: http://hqmeded-ecg.blogspot.com/2016/11/paper-published-terminal-qrs-distortion.html 2016
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27658331 Lee et al.
- Science Direct: Terminal QRS Distortion
Questions? Contact Us
Enjoy this Post? Learn more by signing up for one of our 12-lead ECG or ECG Rhythm CME courses! Save 10% with promo code: QRS10 at checkout.
-
12-lead ECG Interpretation Textbook
$64.99 -
12-lead ECG Interpretation Workbook
$48.50 -
12-lead Textbook, Workbook & HEART Ruler Packet
$124.00Original price was: $124.00.$110.00Current price is: $110.00. -
50 ECG Case Studies Course (13 Hrs CME)
$145.00 -
50 ECG Case Study & STEMI Review Combo Pack (19 Hrs CME)
$235.00Original price was: $235.00.$199.00Current price is: $199.00. -
50 ECG Case Study Value Packet | Textbook, Workbook, HEART Ruler + 13 Hours Cat I CME
$273.49Original price was: $273.49.$136.75Current price is: $136.75. -
ACLS Prep Course (3 Hrs CME)
$65.00 -
Advanced 12-Lead ECG Interpretation Course (30 Hrs CME)
$499.00 -
Animated ECG Rhythm Interpretation Course (9 Hrs CME/CE)
$125.00








1 Response